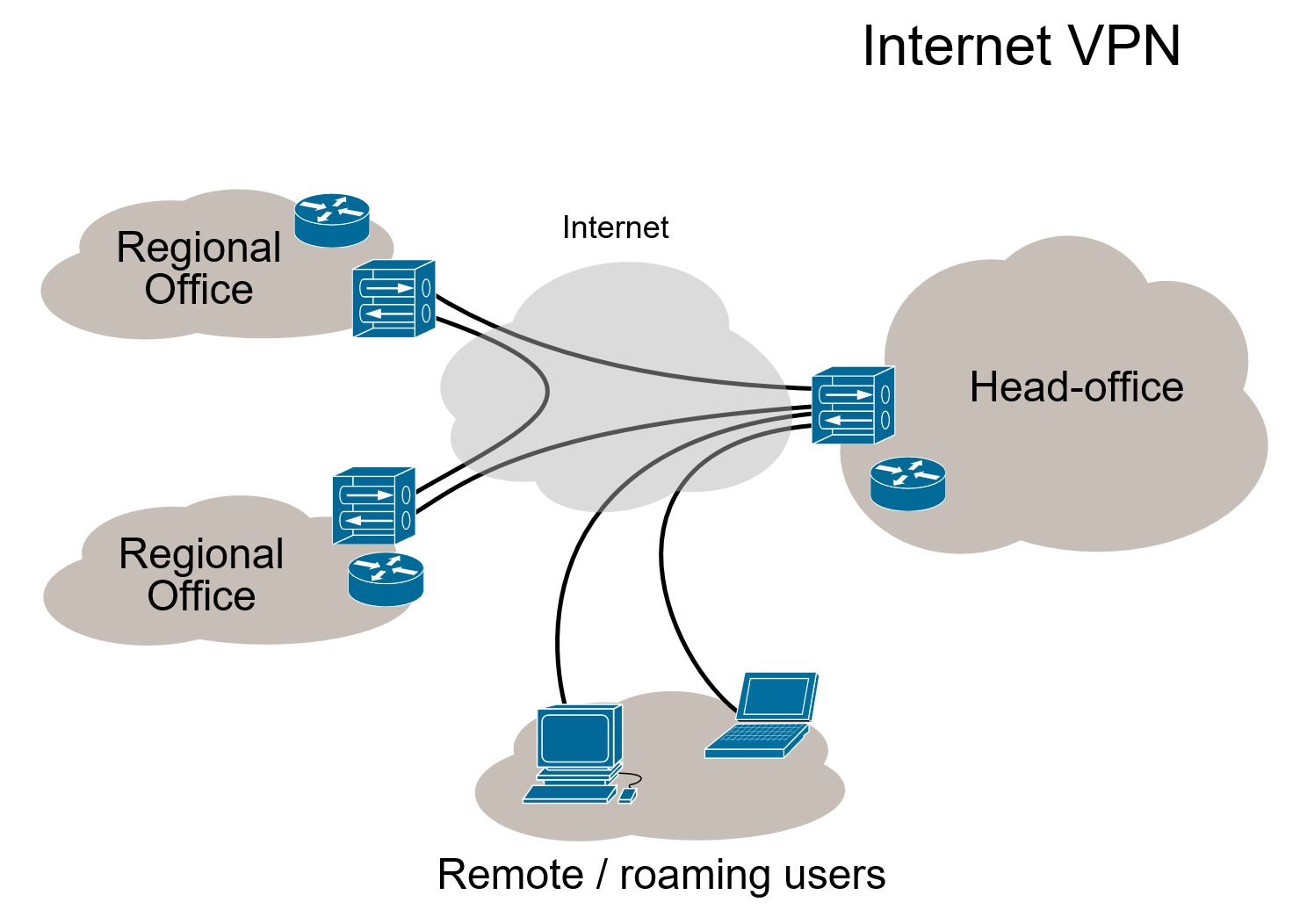
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) extends the local network through a public network.
Presentation
VPN allows users to send and receive data over a shared or public network as if their computers were directly connected to the local network.
The “private” nature of the connection is that the data passing through the VPN is not visible on the original network due to encryption. Encryption is a commonly used feature of VPN, but it can also be used without encryption to separate different data streams or to simplify the logical structure of a network.
The VPN feature is often built into routers, but in many cases is implemented in software.
Practical applications
A VPN is a common application where employees can securely access a company’s internal network remotely: an encrypted channel can be created over the Internet between an employee’s computer and the company’s server.